Requests
You can configure CRUD operations through Web Services Proxy to replace PII data from original requests and responses. Requests and responses which are not mentioned in configuration will remain as is.
CRUD requests
Now when we have created the schema for regulated data, we can proceed with implementation of data residency capabilities in our web application. As the quickest and simplest solution for capturing regulated data and its saving to the InCountry platform we can choose Web Services.
When implementing Web Services for handling requests containing regulated data, you need to consider the following limitations:
-
JSON or x-www-form-urlencoded data structure. The request and response body must be in the JSON or x-www-form-urlencoded format only. Other data formats will be ignored and will be passed as is.
-
Bulk creation or update of records is not supported.
-
Field-based policy is not supported intentionally. Web Services does not regulate access to specific fields of the record for each user, considering user-specific permissions. Web Services just unredacts the response body that your application backend returns. Your application backend must consider this and must return within the response body only the fields the user can view, other fields must be removed. For example, the user is not intended to see the Salary field when viewing the list of users, so the application backend when returning the response body must exclude the Salary field, and otherwise Web Services may reveal the actual clear-text values.
-
The ID of a newly created record must be present in the response to the request for creating a record.
-
The ID of the record should be present in the body of a request or in the URL request (for example,
PUT /customers/id123) in data requests for updating records. -
The ID of the record should be present in the request URL for data requests for deleting records.
All integrations with the InCountry DRaaS platform require a TLS handshake with the SNI (Server Name Indication) extension enabled. Please make sure that your TLS client is configured accordingly!
Let’s get started with Web Services, you need to do the following preliminary steps:
-
Open the country where you want to implement Web Services.
-
Create a service.
Having created a service, we can proceed with implementing endpoints through which we will route our application requests containing regulated data.
Creation of Web Services endpoints
Setting up a Web Services configuration
-
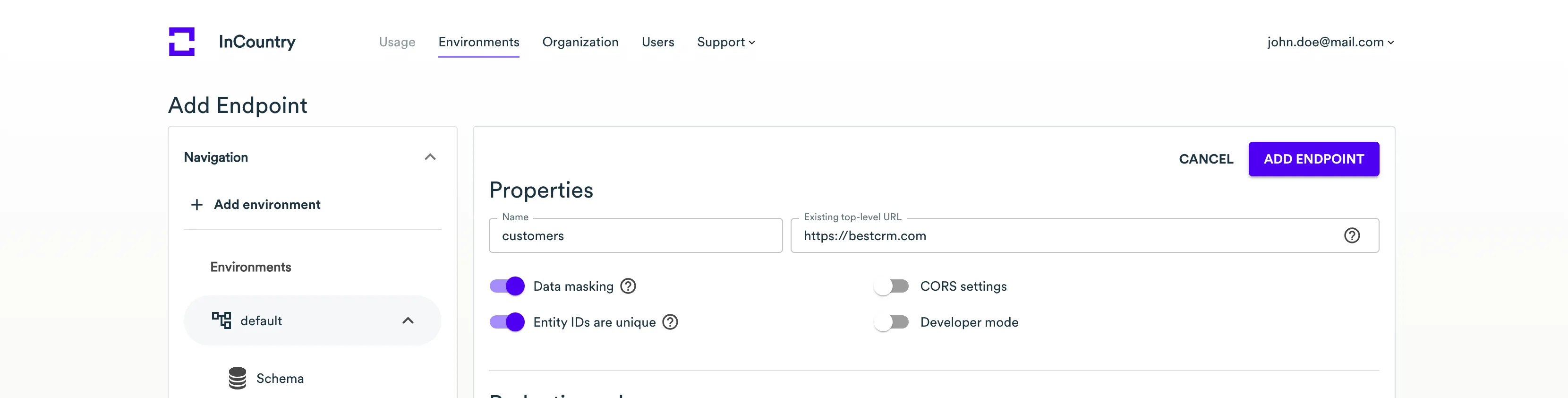
Create a new Web Services endpoint.
-
Enter the endpoint name.
-
Enter the URL of your web application.

Before implementing data residency capabilities within this web application, let’s identify data requests that handle regulated data. In the case of our web application, all the requests deal with customer data and regulated values in particular. Let’s check how an original request looks like and create redaction and unredaction rules for each request.
Creating a new customer
| URI | HTTP method |
|---|---|
/api/customers | POST |
The request payload looks as follows:
{
"firstName": "Liu",
"lastName": "Chang",
"email": "liu_chang@qq.com",
"phone": "+8613260710890",
"vehicle": "Haval",
"yearlySpending": 123,
"country": "cn"
}
The response body looks as follows:
{
"id" : "85d117f8-1b1a-11ee-be56-0242ac120002",
"firstName": "Liu",
"lastName": "Chang",
"email": "liu_chang@qq.com",
"phone": "+8613260710890",
"vehicle": "Haval",
"yearlySpending": 123,
"country": "cn"
}
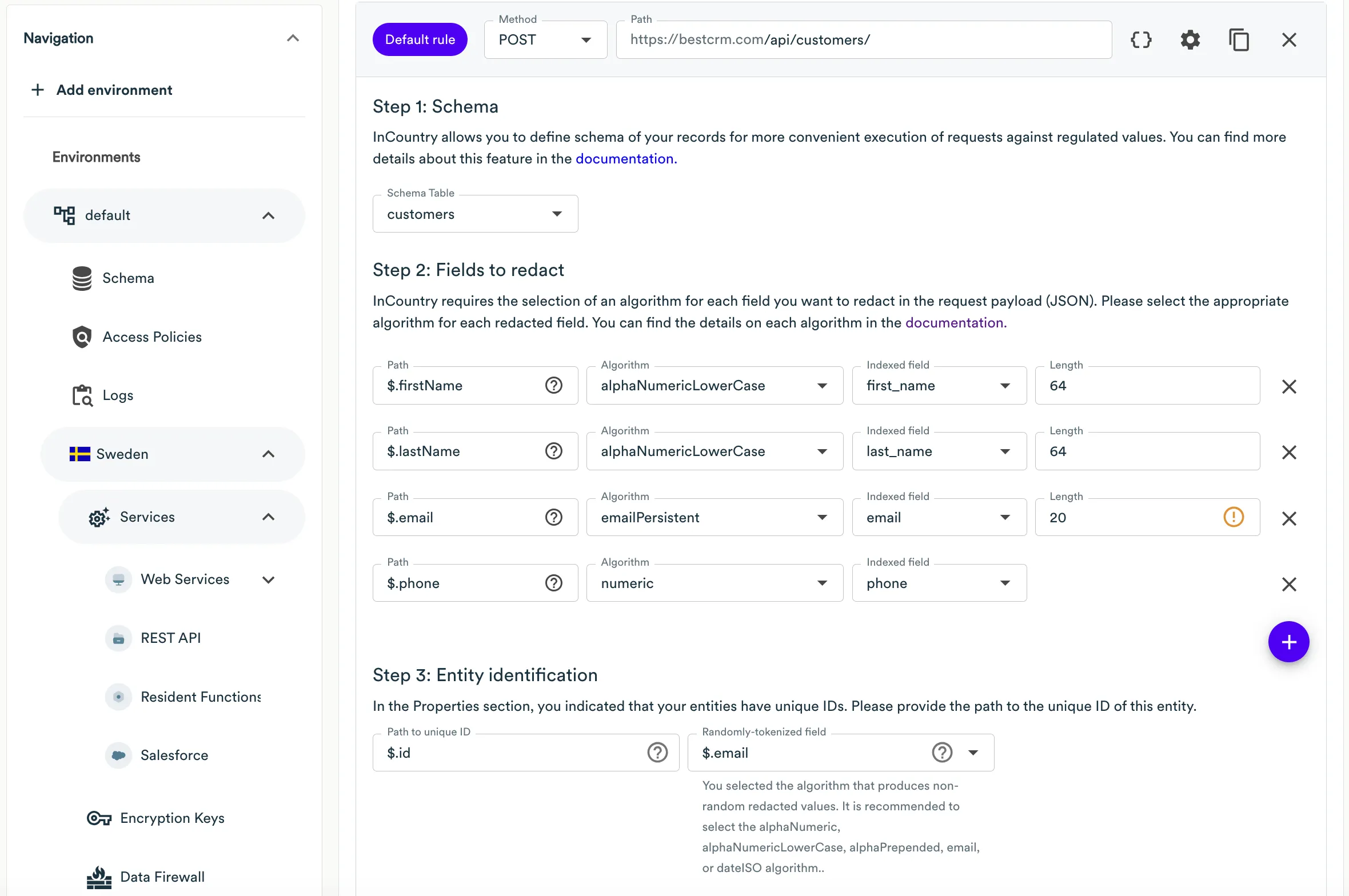
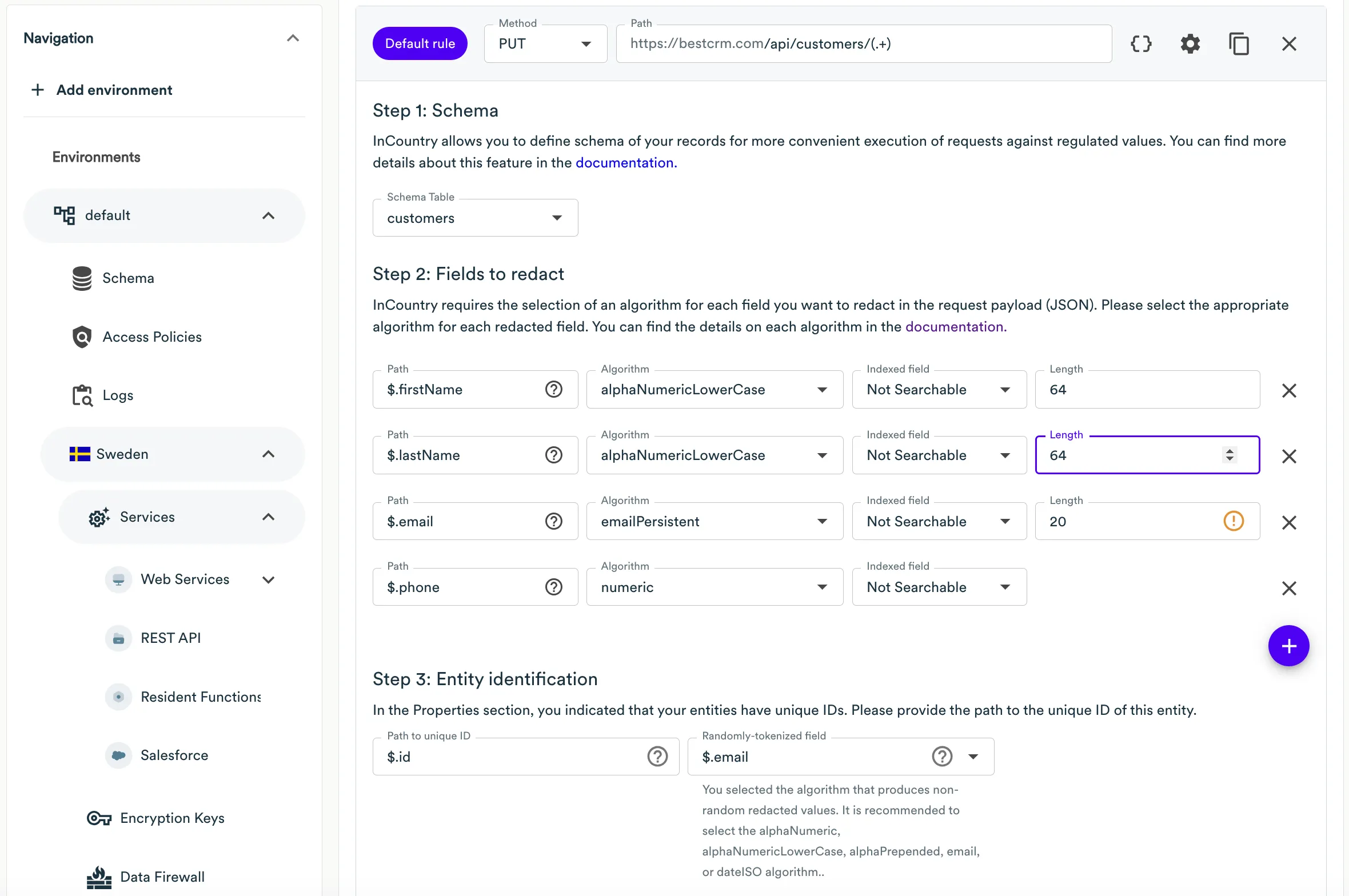
Updating a customer
| URI | HTTP method |
|---|---|
/api/customers/{customer_id} | PUT |
The request payload looks as follows:
{
"id": "85d117f8-1b1a-11ee-be56-0242ac120002",
"firstName": "Liu",
"lastName": "Chang",
"email": "liu_chang@qq.com",
"phone": "+8613260710890",
"vehicle": "Changan",
"yearlySpending": 123,
"country": "cn"
}
The response body looks as follows:
{
"id" : "85d117f8-1b1a-11ee-be56-0242ac120002",
"firstName": "Liu",
"lastName": "Chang",
"email": "liu_chang@qq.com",
"phone": "+8613260710890",
"vehicle": "Changan",
"yearlySpending": 123,
"country": "cn"
}
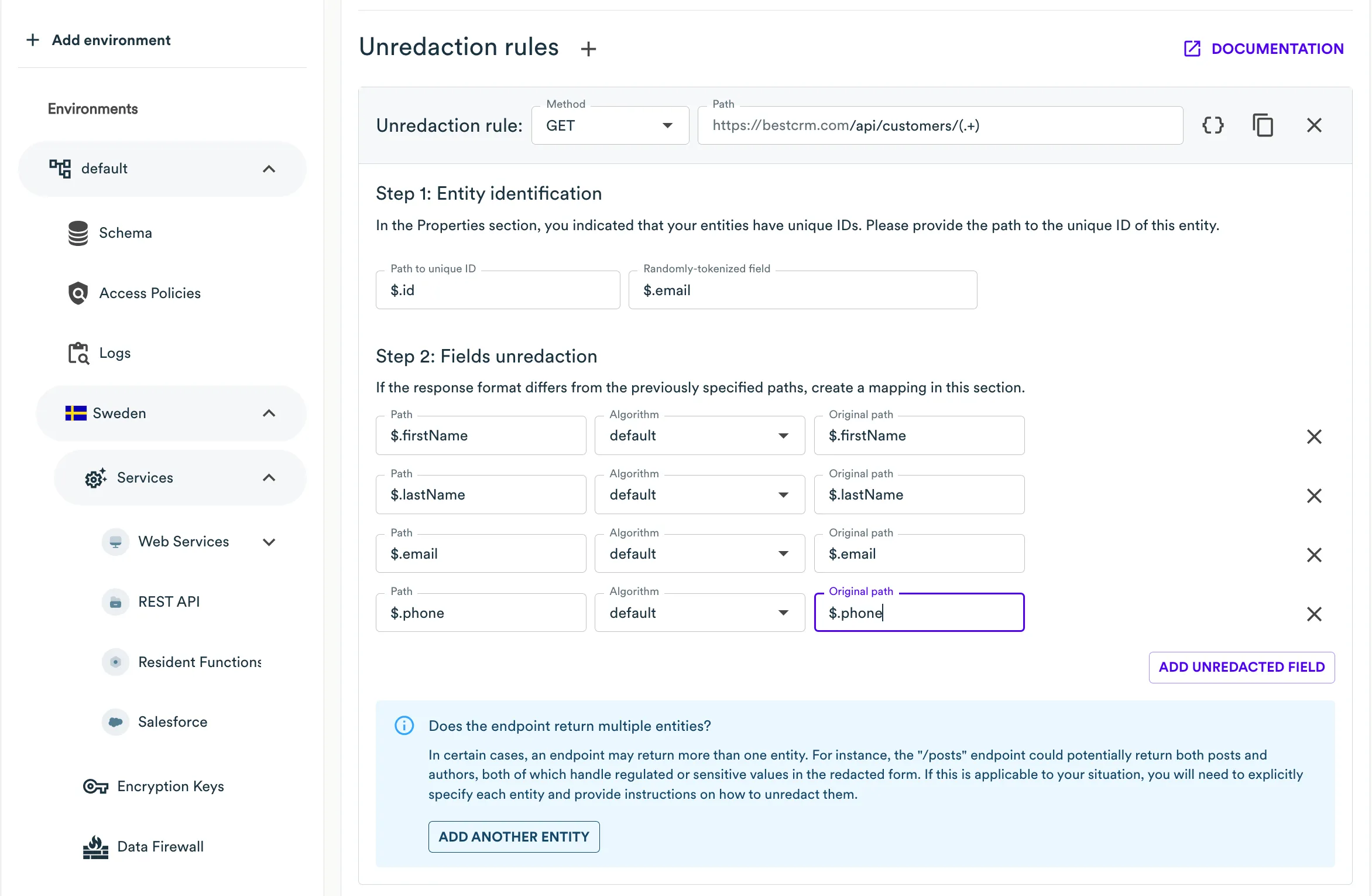
Viewing a customer
| URI | HTTP method |
|---|---|
/api/customers/{customer_id} | GET |
The response body looks as follows:
{
"id" : "85d117f8-1b1a-11ee-be56-0242ac120002",
"firstName": "Liu",
"lastName": "Chang",
"email": "liu_chang@qq.com",
"phone": "+8613260710890",
"vehicle": "Changan",
"yearlySpending": 123,
"country": "cn"
}
Deleting a customer
| URI | HTTP method |
|---|---|
/api/customers/{customer_id} | DELETE |

Save the Web Services endpoint.
For more details of Web Services configuration please see Portal documentation